

Operators - special symbols that specify the type of operation or calculation to be performed.Functions - predefined formulas in Excel that perform calculations using the values supplied in their arguments.Names - defined name for a cell range, constant, table, or function, for example =SUM(my_name).For example, to sum values in all cell between A1 and A5, inclusive, use this formula: To refer to data in two or more contiguous cells, use a range reference like A1:A5. Cell references - reference to a cell containing the value you want to use in your Excel formula, e.g.Constants - numbers or text values that you enter directly in a formula, like =2*3.Depending on the formula type that you create, it can include any or all of the following parts: When you make a formula in Excel, you can use different elements to supply the source data to the formula and indicate what operators should be performed on those data.

Press the Enter key to complete the formula.Type the entire equation: =B1+B2+B3+B4+B5.For example, to add up values in cells B1 through B5, you can either: After the equal symbol, you enter either a calculation or function.All Excel formulas begin with an equal sign (=).Though Microsoft has introduced a handful of new functions over the years, the concept of Excel spreadsheet formulas is the same in all versions of Excel 2016, Excel 2013, Excel 2010, Excel 2007 and lower. In MS Excel, formulas are equations that perform various calculations in your worksheets. Cell reference types (absolute, relative, mixed).
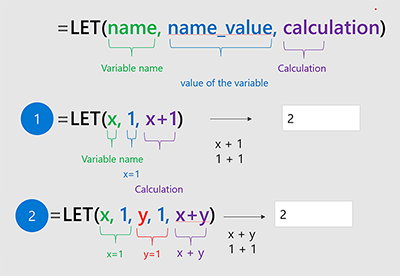
It also provides a number of advanced formula examples for experienced users. Can Microsoft Excel formulas be easy to learn? Yep! This tutorial explains the very basics of Excel formulas for beginners, with detailed steps on how to write and use them.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
